| USING A ROOT DOMAIN WITH YOUR WEBSITE
If you you want to use your root (base) domain, ie without the user having to type a host name like "www" - in the same way that if you type "apple.com" into your web-browser it redirects to (displays) "www.apple.com", as it does also for the likes of "facebook.com", "google.com" etc - then you need to do something special.
The days of pointing the root domain directly to a single IP address using an DNS A record are fading fast.
You can't use a CNAME record as it will effect all your DNS records, including your MX email records.
To deal with it, most domain registrars/hosters provide a URL forwarding service. If your registrar doesn't support it, you can always use the Amazon Web Services Route53 service to host your domain.
Essentially they set up an DNS A record that points to a http service that they are running - it then redirects to the "www" host - ie user types in mydomain.com and it gets redirected to www.mydomain.com - which has the CNAME reference to the ibCom platforms array of load balancers with many IP addresses (not just one, like in the past).
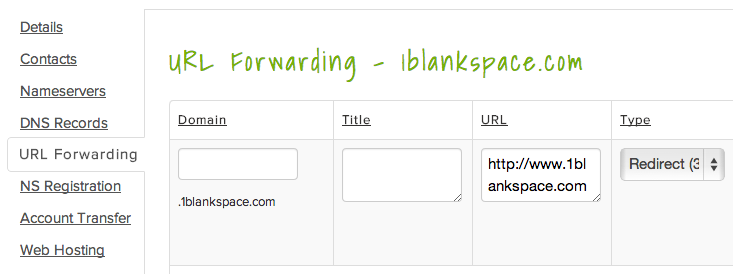
EXAMPLE URL FORWARDING SET UP:
Typically you can pick type "301" (permanent redirect) or "302" (once off redirect, happens each time they revisit) - pick "301" if not sure.
If your registrar doesn't support URL forwarding, then:
- Change registrar - eg to someone like "name.com" (not an endorsement)
- Use a service like "https://www.rootredirect.com" (not an endorsement)
|